The CPU (Central Processing Unit) is responsible for processing and executing instructions. This article helps you understand how the CPU interacts with the rest of the device and what makes them and the computing process so designed.
What makes a CPU a CPU?
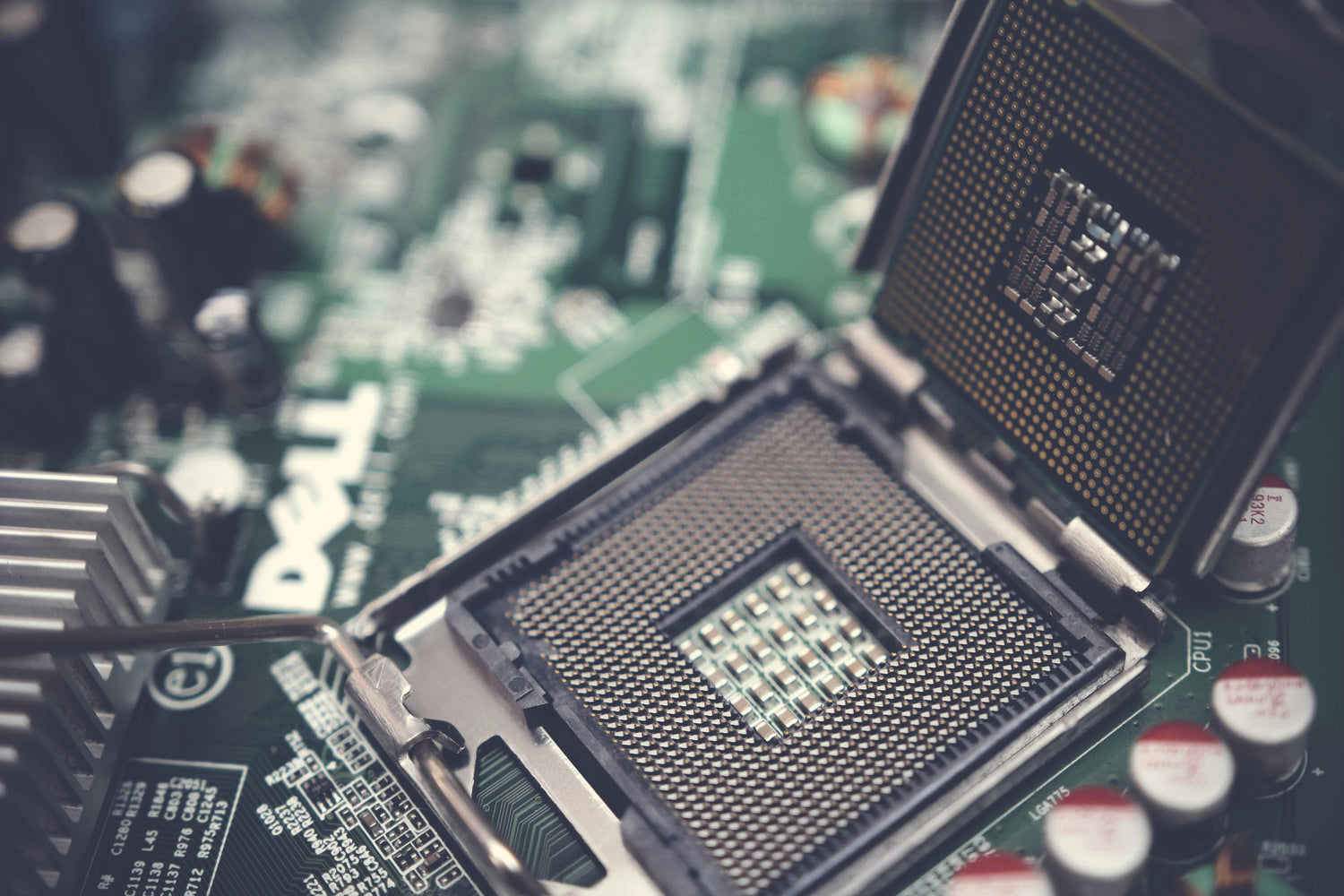
The CPU is the core component that defines a computing device, but it's not the only component, it's just the brain. The chip is located in a special socket (slot) on the main circuit board (motherboard or motherboard) inside the device. It is significantly different from memory where information is temporarily stored. It's also separate from the graphics card, or graphics chip, which renders all video and 3D graphics displayed on the screen.
CPUs are built by placing billions of tiny transistors on a single computer chip. These transistors allow it to perform calculations to run programs stored in the system's memory. They're actually tiny gates that open or close, thus conveying zero or zero, which translates to everything you do with the device, whether it's watching a video or writing an email.
One of the most common advances in CPU technology is making these transistors smaller and smaller. This led to an increase in CPU speed over several decades, often referred to as Moore's Law
In modern devices, a desktop or laptop computer has a dedicated CPU that performs many processing functions for the system. Instead, mobile devices and some tablets use a system-on-a-chip (SoC), a chip that contains their CPU and other components. Both Intel and AMD offer CPUs with graphics chips and memory, meaning they can perform more than just standard CPU functions.
What does the CPU actually do?
The core of the CPU takes instructions from a program or application and performs calculations. The process is divided into three key stages: acquisition, decoding and execution. The CPU fetches the instruction from RAM, decodes its actual meaning, and then uses the relevant part of the CPU to execute the instruction.
The instructions or calculations performed may involve basic arithmetic, comparing certain numbers or moving them around in memory. Since everything in a computing device is represented by the number 01, these simple tasks are equivalent to the work of the CPU. From starting Windows to watching Bilibili videos, everything is easy.
In modern systems, the CPU can't do everything, but it still has to give the number of functions it needs to specialized hardware. For example, it tells the graphics card to display an explosion effect because you clicked a thunderbolt, or it tells the hard drive to transfer an Office document into the system's RAM for faster access.
How important is the CPU?
Although the CPU is less important to overall system performance than it once was, it still plays an important role in running your device. Since it is only responsible for executing commands within a program, the faster the CPU, the faster many applications will run.
That said, a fast CPU isn't everything. Processors, no matter how powerful, can't easily render the latest 3D games, nor can they store information. This is where other components like the graphics card and memory come into play.
In short, the CPU is not everything, but it is very important. Generally, a faster CPU means your system or device will run faster. At least it won't be a bottleneck in itself. Multiple cores and threads help you do more at once.
What makes a CPU a CPU?
The CPU is the core component that defines a computing device, but it's not the only component, it's just the brain. The chip is located in a special socket (slot) on the main circuit board (motherboard or motherboard) inside the device. It is significantly different from memory where information is temporarily stored. It's also separate from the graphics card, or graphics chip, which renders all video and 3D graphics displayed on the screen.
CPUs are built by placing billions of tiny transistors on a single computer chip. These transistors allow it to perform calculations to run programs stored in the system's memory. They're actually tiny gates that open or close, thus conveying zero or zero, which translates to everything you do with the device, whether it's watching a video or writing an email.
One of the most common advances in CPU technology is making these transistors smaller and smaller. This led to an increase in CPU speed over several decades, often referred to as Moore's Law
In modern devices, a desktop or laptop computer has a dedicated CPU that performs many processing functions for the system. Instead, mobile devices and some tablets use a system-on-a-chip (SoC), a chip that contains their CPU and other components. Both Intel and AMD offer CPUs with graphics chips and memory, meaning they can perform more than just standard CPU functions.
What does the CPU actually do?
The core of the CPU takes instructions from a program or application and performs calculations. The process is divided into three key stages: acquisition, decoding and execution. The CPU fetches the instruction from RAM, decodes its actual meaning, and then uses the relevant part of the CPU to execute the instruction.
The instructions or calculations performed may involve basic arithmetic, comparing certain numbers or moving them around in memory. Since everything in a computing device is represented by the number 01, these simple tasks are equivalent to the work of the CPU. From starting Windows to watching Bilibili videos, everything is easy.
In modern systems, the CPU can't do everything, but it still has to give the number of functions it needs to specialized hardware. For example, it tells the graphics card to display an explosion effect because you clicked a thunderbolt, or it tells the hard drive to transfer an Office document into the system's RAM for faster access.
How important is the CPU?
Although the CPU is less important to overall system performance than it once was, it still plays an important role in running your device. Since it is only responsible for executing commands within a program, the faster the CPU, the faster many applications will run.
That said, a fast CPU isn't everything. Processors, no matter how powerful, can't easily render the latest 3D games, nor can they store information. This is where other components like the graphics card and memory come into play.
In short, the CPU is not everything, but it is very important. Generally, a faster CPU means your system or device will run faster. At least it won't be a bottleneck in itself. Multiple cores and threads help you do more at once.